A Comparison of different crossover operators in genetic algorithms for clusters shortest-path tree problem
A Comparison of different crossover operators in genetic algorithms for clusters shortest-path tree problem
Cosmin Sabo, Petrică Claudiu Pop, Adrian Petrovan
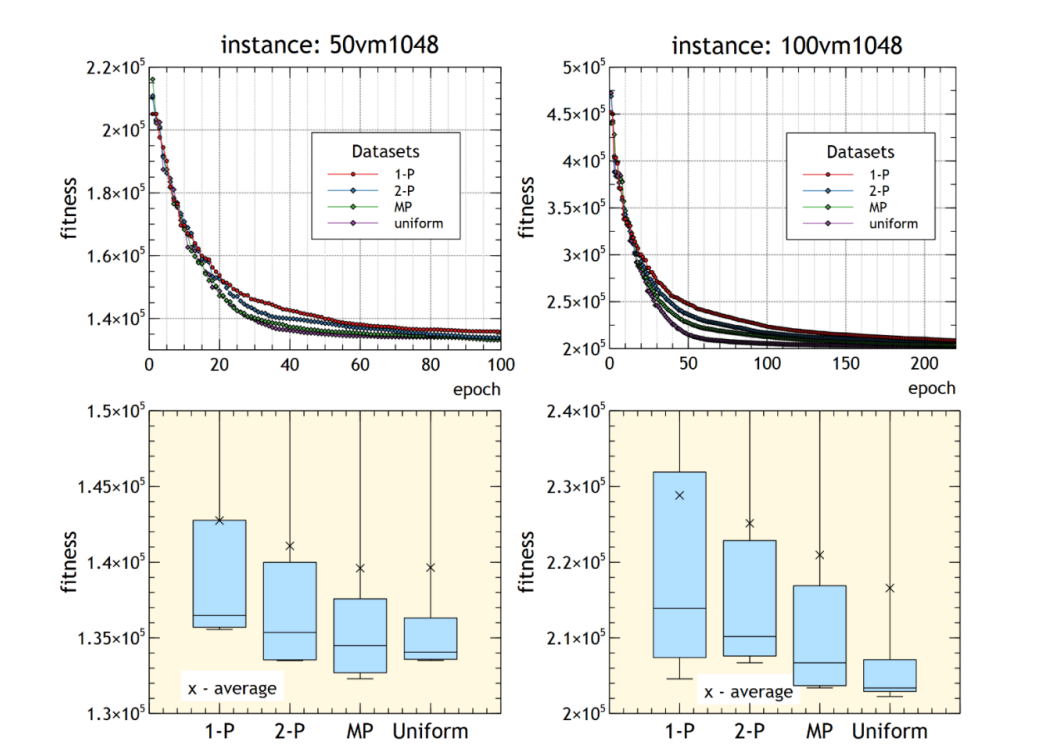
Abstract. The clustered shortest-path tree (CluSPT) problem is an extension of the classical shortest path problem, given a graph with the nodes partitioned into several mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive clusters looks for a shortest-path spanning tree from a predefined source node to all the other nodes of the graph, with the property that every cluster should generate a connected subgraph. Due to the problem’s complexity, different metaheuristic algorithms have been proposed to find good-quality solutions within reasonable computational effort. Between these methods, evolutionary algorithms proved to be the most efficient method for solving the CluSPT problem. The present paper aims to investigate the
effect of different crossover operators on the quality of the achieved solutions by the hybrid genetic algorithm proposed by Petrovan et al. [10], the current state-of-the-art algorithm for the CluSPT problem. Computational experiments were conducted on 46 benchmark instances from the literature. In our computational experiments, we used four variants of crossover operators, which allowed us to perform a comprehensive analysis and comparison of the achieved results, enabling us to thoroughly examine the impact of the crossover operators on the obtained results.
Keywords: genetic algorithms, the clustered shortest path tree problem.
Other publications
Guide in Designing an Asynchronous Performance-Centric Framework for Heterogeneous Microservices in Time-Critical Cybersecurity Applications. The BIECO Use Case
The generalized traveling salesman problem (GTSP) is an extension of the classical traveling salesman
problem (TSP), and it is among the most researched combinatorial optimization problems due to its theoretical properties, complexity aspects, and real-life applications in various areas: location-routing problems, material flow design problem, distribution of medical supplies, urban waste collection management, airport selection and routing the courier airplanes, image retrieval and ranking, digital garment manufacturing, etc.
Trend-Enabled Recommender System with Diversity Enhancer for Crop Recommendation
The generalized traveling salesman problem (GTSP) is an extension of the classical traveling salesman
problem (TSP), and it is among the most researched combinatorial optimization problems due to its theoretical properties, complexity aspects, and real-life applications in various areas: location-routing problems, material flow design problem, distribution of medical supplies, urban waste collection management, airport selection and routing the courier airplanes, image retrieval and ranking, digital garment manufacturing, etc.
Evaluation of Feature Selection Methods in Estimation of Precipitation Based on Deep Learning Artificial Neural Networks
Precipitation is the most important element of the water cycle and an indispensable element of water resources management. This paper aims to model the monthly precipitation in 8 precipitation observation stations. The effects and role of different feature weights pre-processing methods (Weight by deviation, Weight by PCA, Weight by correlation, and Weight by Support Vector Machine) on artificial intelligence modeling were investigated.
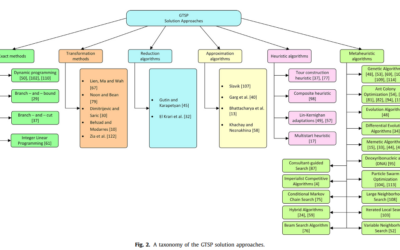
A comprehensive survey on the generalized traveling salesman problem
The generalized traveling salesman problem (GTSP) is an extension of the classical traveling salesman
problem (TSP), and it is among the most researched combinatorial optimization problems due to its theoretical properties, complexity aspects, and real-life applications in various areas: location-routing problems, material flow design problem, distribution of medical supplies, urban waste collection management, airport selection and routing the courier airplanes, image retrieval and ranking, digital garment manufacturing, etc.
A hybrid based genetic algorithm for solving the clustered generalized traveling salesman problem
We study the clustered generalized traveling salesman problem (CGTSP), which is an extension of the generalized traveling salesman problem (GTSP), which in turn generalizes the well-known traveling salesman problem (TSP).

0 Comments