KPIs
Explore the dedicated page for an insightful overview of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) publications, showing the progress and impact of the COSA Project.

- O1 Number of foreign researchers involved
- O2 Number of co-publications
- O3 Number of scientific articles in journals
- O4 Number of articles presented to international conferences
- O5 Number of articles published in the top 25% cited publications
- O6 Researchers involved in the project
- O7 Researchers working in Romanian research organizations (research centers) receiving support (full-time equivalent)
- O8 Projects submitted by Romanian research organizations that have reached at least the funding threshold for Horizon Europe competitions
- O9 Projects submitted in national research, development, and innovation programs
- O10 Number of submitted patents
- O11 Number of postdocs in the research team
- O12 Number of PhD students in the research team
- O13 Number of frameworks developed and validated
- O14 Number of intelligent algorithms developed and integrated within COSA
- O15 Number of use cases
- O16 Amount of data collected during the project (thousands of entries)
- O17 Number of sensors connected to the COSA framework
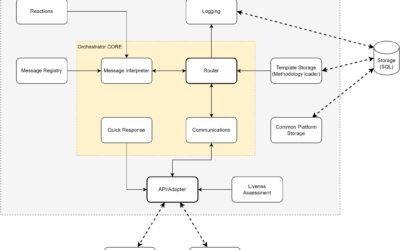
Guide in Designing an Asynchronous Performance-Centric Framework for Heterogeneous Microservices in Time-Critical Cybersecurity Applications. The BIECO Use Case
The generalized traveling salesman problem (GTSP) is an extension of the classical traveling salesman
problem (TSP), and it is among the most researched combinatorial optimization problems due to its theoretical properties, complexity aspects, and real-life applications in various areas: location-routing problems, material flow design problem, distribution of medical supplies, urban waste collection management, airport selection and routing the courier airplanes, image retrieval and ranking, digital garment manufacturing, etc.
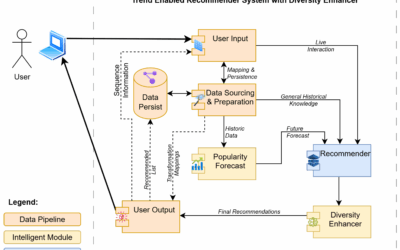
Trend-Enabled Recommender System with Diversity Enhancer for Crop Recommendation
The generalized traveling salesman problem (GTSP) is an extension of the classical traveling salesman
problem (TSP), and it is among the most researched combinatorial optimization problems due to its theoretical properties, complexity aspects, and real-life applications in various areas: location-routing problems, material flow design problem, distribution of medical supplies, urban waste collection management, airport selection and routing the courier airplanes, image retrieval and ranking, digital garment manufacturing, etc.
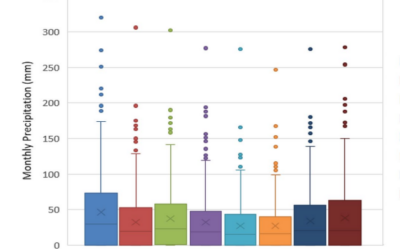
Evaluation of Feature Selection Methods in Estimation of Precipitation Based on Deep Learning Artificial Neural Networks
Precipitation is the most important element of the water cycle and an indispensable element of water resources management. This paper aims to model the monthly precipitation in 8 precipitation observation stations. The effects and role of different feature weights pre-processing methods (Weight by deviation, Weight by PCA, Weight by correlation, and Weight by Support Vector Machine) on artificial intelligence modeling were investigated.
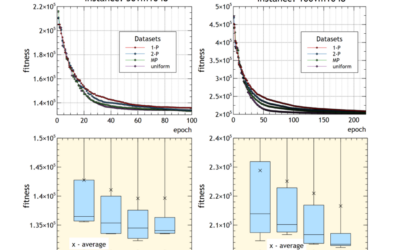
A Comparison of different crossover operators in genetic algorithms for clusters shortest-path tree problem
The clustered shortest-path tree (CluSPT) problem is an extension of the classical shortest path problem, given a graph with the nodes partitioned into several mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive clusters looks for a shortest-path spanning tree from a predefined source node to all the other nodes of the graph, with the property that every cluster should generate a connected subgraph.
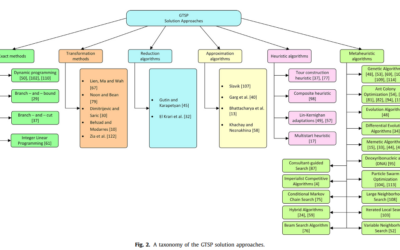
A comprehensive survey on the generalized traveling salesman problem
The generalized traveling salesman problem (GTSP) is an extension of the classical traveling salesman
problem (TSP), and it is among the most researched combinatorial optimization problems due to its theoretical properties, complexity aspects, and real-life applications in various areas: location-routing problems, material flow design problem, distribution of medical supplies, urban waste collection management, airport selection and routing the courier airplanes, image retrieval and ranking, digital garment manufacturing, etc.
A hybrid based genetic algorithm for solving the clustered generalized traveling salesman problem
We study the clustered generalized traveling salesman problem (CGTSP), which is an extension of the generalized traveling salesman problem (GTSP), which in turn generalizes the well-known traveling salesman problem (TSP).